Trusted Proxy: How it Works
Trusted Proxy: How it Works
See also: Choosing the Right Authentication Profile , Proxying and Caching with Enfold Proxy and the Single Signon Troubleshooting Checklist . See also the current Enfold Proxy documentation.
Trusted Proxy vs. No Trusted Proxy Authentication
When choosing authentication profiles in Enfold Server(ES), you need to decide whether to choose a profile with Trusted Proxy Authentication. That happens if the NTLM authentication is taking place on a different machine. One common scenario is for Enfold Server to exist on machine 1 and IIS and Enfold Proxy(EP) on machine 2.
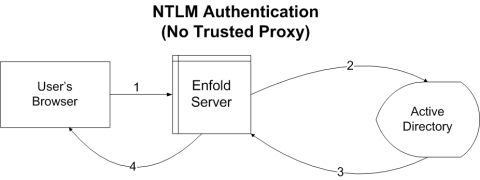
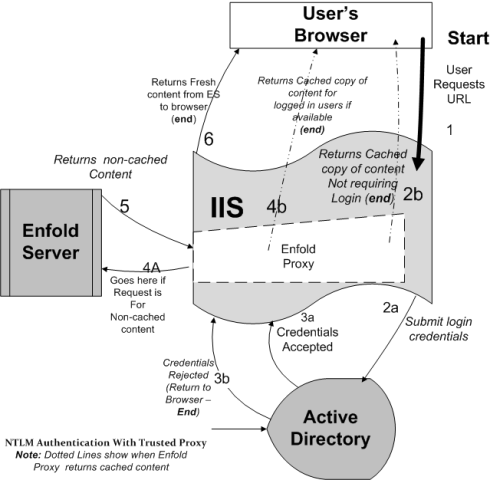
Here is a diagram that shows how authentication differs in each case.
In the first scenario, NTLM with No Trusted Proxy Authentication, Enfold Server handles NTLM authentication. Examples of authentication profiles for this: Active Directory Users and Groups with Cookie Authentication, Active Directory Users and Groups with Integrated Windows Security, Active Directory Users with Integrated Windows Security, Active Directory Users with Cookie Authentication.
In the second scenario, NTLM with Trusted Proxy Authentication, Enfold Server does not handle NTLM authentication. Instead, IIS/EP handles the request and performs authentication, then forwards the request to Enfold Server. Enfold Proxy is an ISAPI filter within IIS. EP is not involved in the actual authentication (although it receives a header which identifies the user which authenticated). EP's main job is to translate URLs from Enfold Server and to arrange for cached copies of web resources to be available so IIS doesn't have to keep requesting them from Enfold Server. Examples of authentication profiles for this: Active Directory Users with Trusted Proxy Authentication, Active Directory Users and Groups with Trusted Proxy Authentication.
The third scenario involves cookie-based authentication or authentication through LDAP. For the most part Enfold Server handles all the authentication. Examples of authentication profiles for this: Default Plone with Cookie Authentication, LDAP Users and Groups with Cookie Authentication, LDAP Users with Cookie Authentication See Authentication - Other Scenarios